Real-Time Tracking of Renewable Carbon Content with AI-aided Approaches During Co-Processing of Biofeedstocks
Applied Energy,
Liang Cao, Jianping Su, Jack Saddler, Yankai Cao, Yixiu Wang, Gary Lee, Lim C. Siang, Robert Pinchuk, Jin Li, R. Bhushan Gopaluni
[PDF]
Abstract
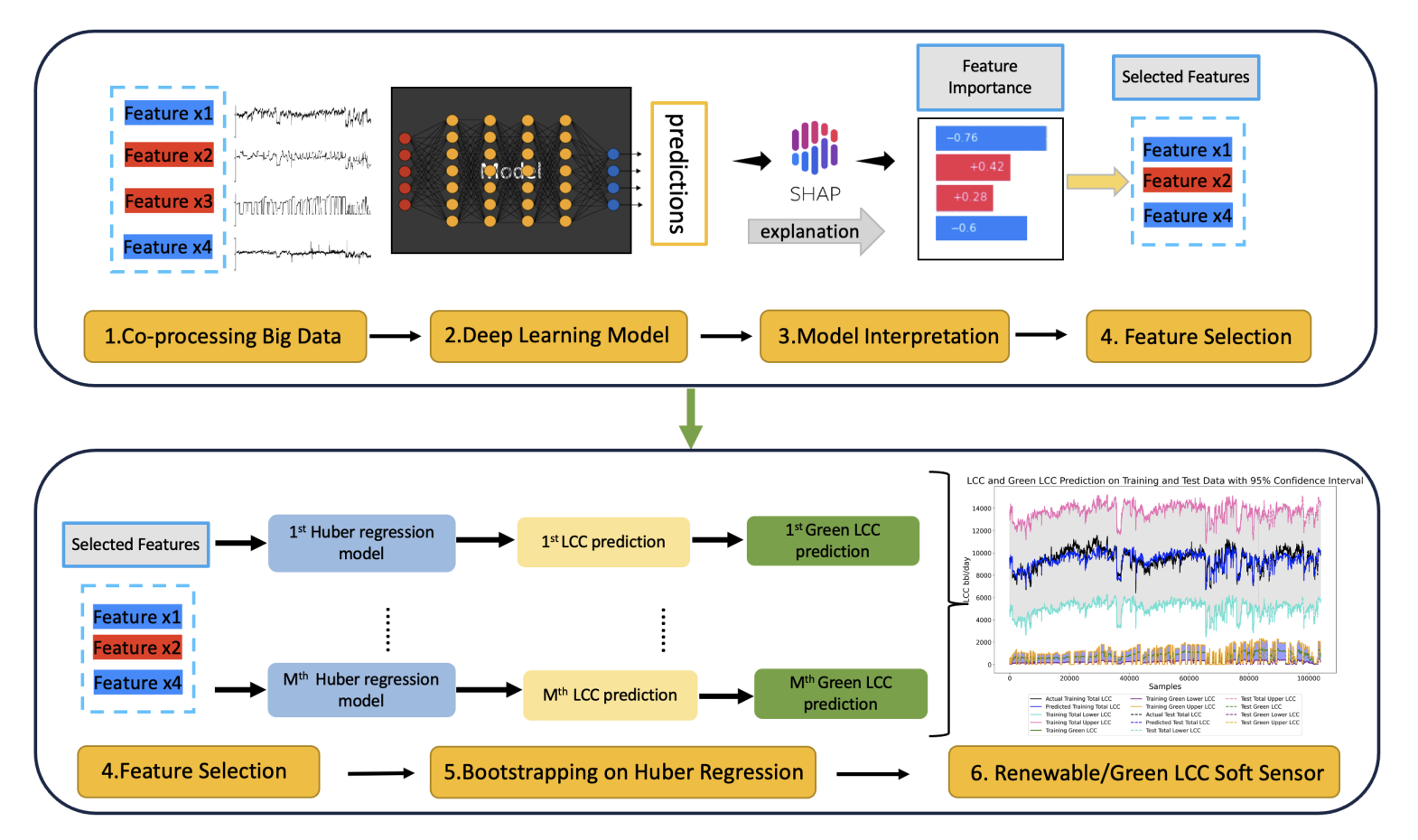
Decarbonization of the oil refining industry is essential for reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change. Co-processing bio feed at existing oil refineries is a promising strategy for achieving this goal. However, accurately quantifying the renewable carbon content of co-processed fuels can be challenging due to the complex process involved. Currently, it can only be achieved through expensive offline 14C measurements. To address this issue, with high-quality and large-scale commercial data, our study proposes a novel approach that utilizes data-driven methods to build inferential 1 sensors, which can estimate the real-time renewable content of biofuel products. We have collected over 1,000,000 co-processing data points from refineries under different bio feed co-processing ratios and operational conditions—the largest dataset of its kind to our knowledge. We use interpretable deep neural networks to select model inputs, then apply robust linear regression and bootstrapping techniques to estimate renewable content and confidence interval. Our method has been validated with four previous 14C measurements during co-processing at the fluid catalytic cracker. This novel methods provides a practical solution for the industry and policymakers to quantify renewable carbon content and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy system
Read or Download: PDF