Interpretable Industrial Soft Sensor Design Based on Informer and SHAP
In Proceedings of the 12th IFAC International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes (ADCHEM),
Liang Cao, Xiaolu Ji, Yankai Cao, Yi Luo, Yixiu Wang, Lim C. Siang, Jin Li, R. Bhushan Gopaluni
[PDF]
Abstract
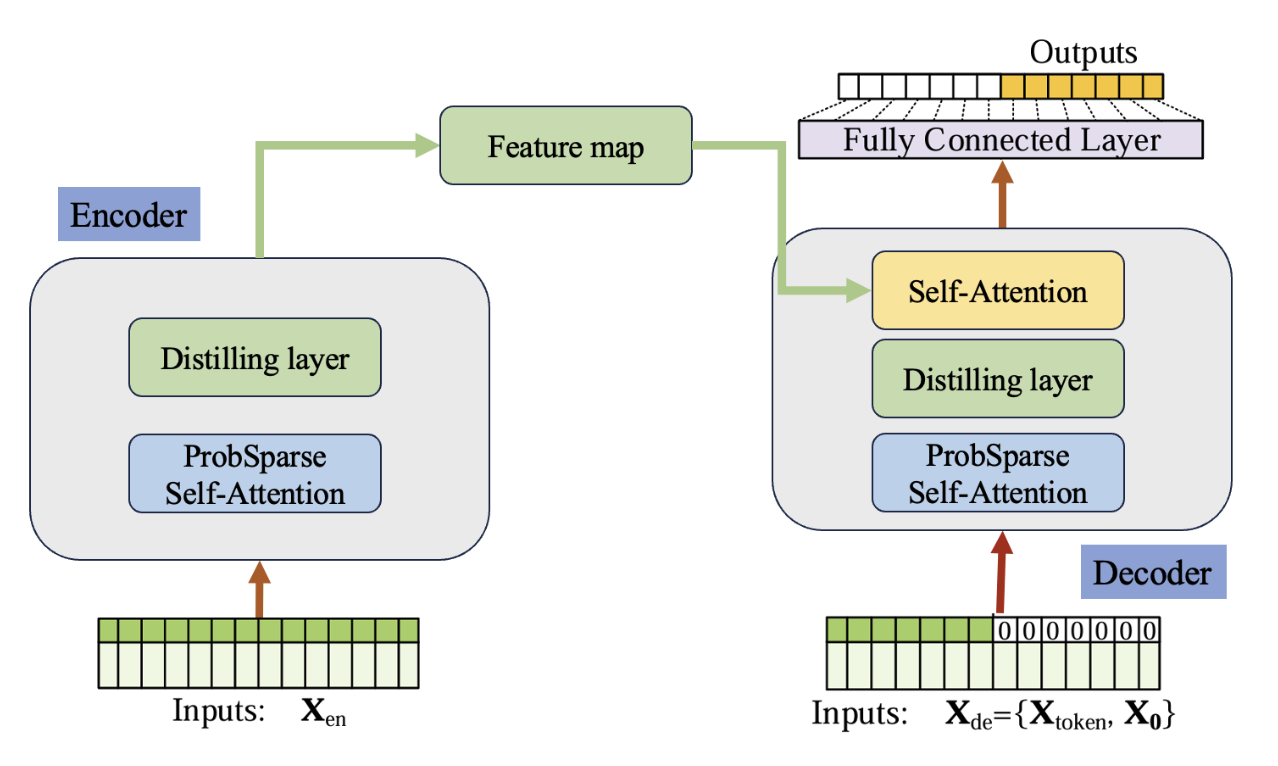
Deep learning models have been widely employed in various domains, yet they have certain limitations when it comes to industrial process applications. The two main challenges are their inability to effectively handle long-sequence predictions and the complexity of their internal structure, which makes it difficult to explain the output of the model. This work aims to build accurate and interpretable soft sensors for industrial processes. The Informer model is used to build accurate soft sensors due to its proficiency in long sequences. Additionally, an interpretable machine learning algorithm, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), is used to infer the global and local contributions of each feature to the predictions. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithms is validated on real industrial fluid catalytic cracker unit data, and the results show that the Informer model has higher accuracy and better long-sequence data prediction ability. Furthermore, the SHAP analysis enhances the model’s utility by providing clear insights into the influence of individual features on the predictions, thereby increasing its transparency and trustworthiness in industrial settings.
Read or Download: PDF