Interpretable Data-Driven Capacity Estimation of Lithium-ion Batteries
In Proceedings of the 12th IFAC International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes (ADCHEM),
Yixiu Wang, Anurakt Kumar, Jiayang Ren, Pufan You, Arpan Seth, R. Bhushan Gopaluni, Yankai Cao
[PDF]
Abstract
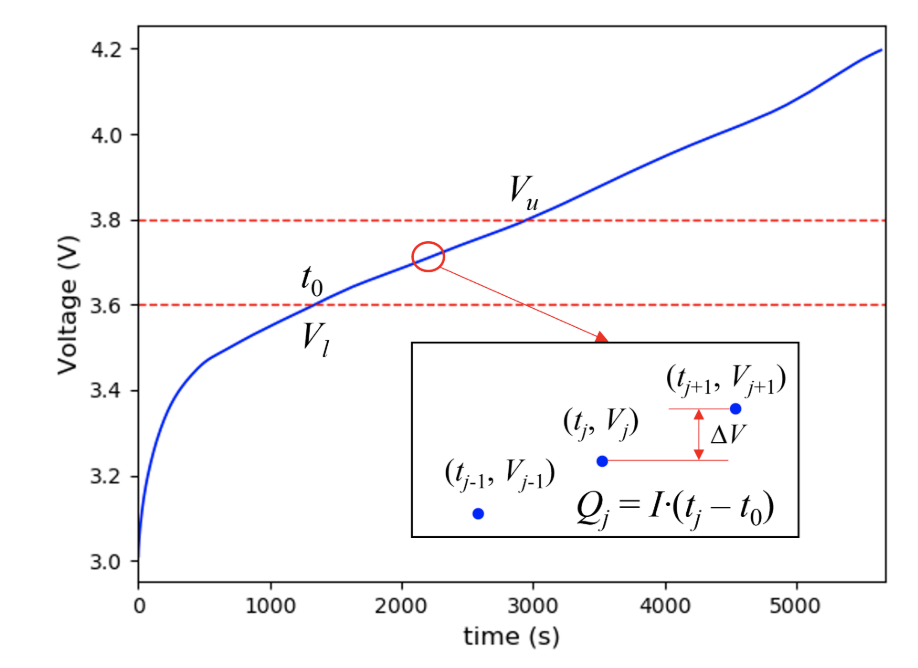
Battery degradation poses a significant challenge for the usage of Lithium-ion batteries, making accurate capacity estimation crucial for efficient operation. Data-driven approaches hold promise for addressing this task, yet their complex structures often lead to overfitting and obscure the decision-making process. The objective of this work is to build a robust and interpretable model for capacity estimation. We propose the utilization of a robust decision tree-based ensemble model, extremely randomized trees (ERT), to accurately estimate battery capacity based on the features extracted from the partial charging curve. The random splits in the tree construction process enhance the model’s generalization ability. Given that the combination of multiple decision trees reduces interpretability, we further employ SHAP to interpret the contributions of each feature to the ERT model’s predictions. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated on a large cycling dataset of Lithium-ion batteries.
Read or Download: PDF