A performance neural network model for conventional solar stills via transfer learning
Applied Energy,
Hashim H. Migaybil, Bhushan Gopaluni
[PDF]
Click to enlarge image.
Abstract
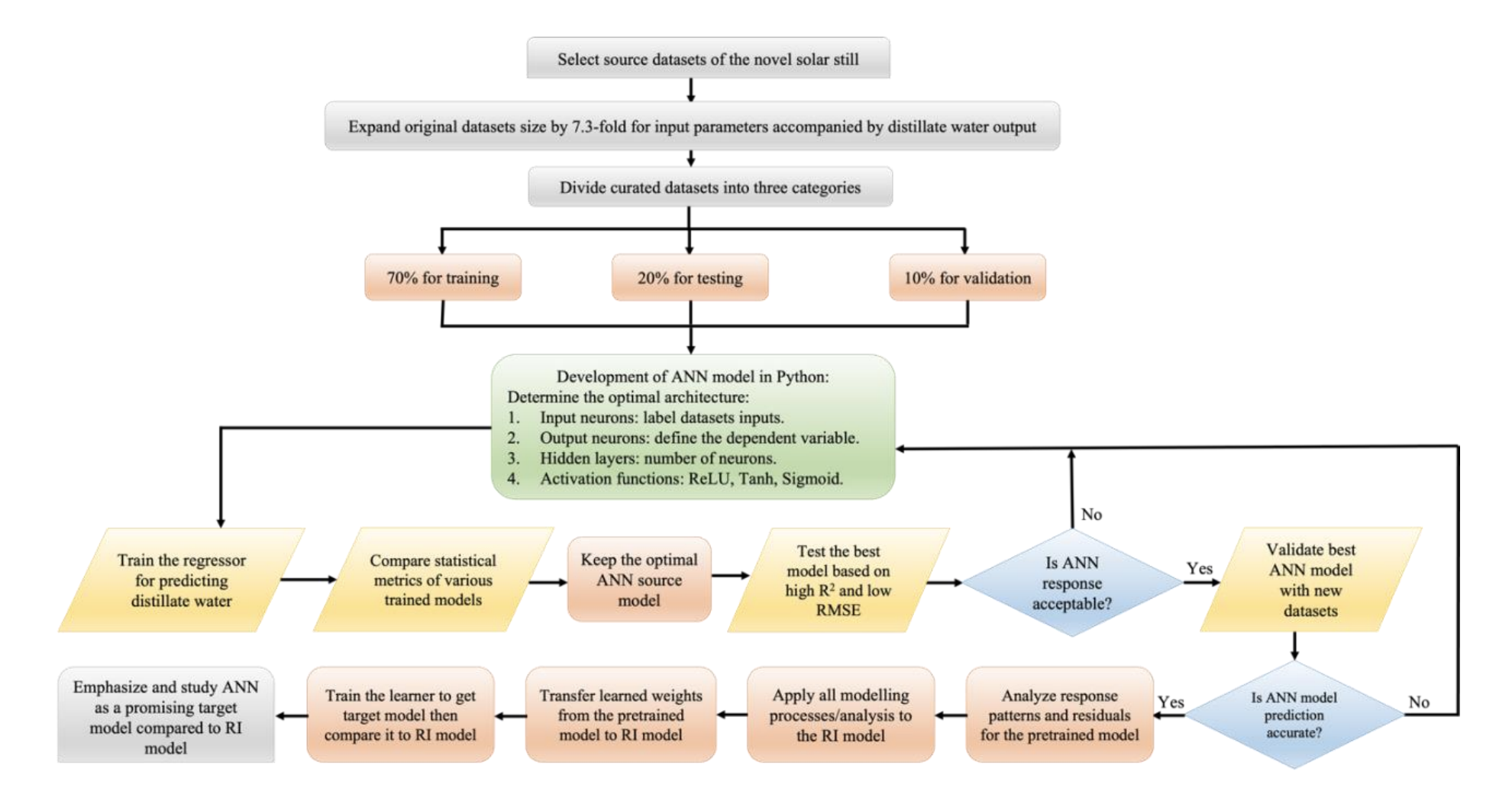
Predictive solar-desalination models are becoming more widespread using ML and AI. However, forecasting solar still water productivity based on numerous designs still needs to be improved. Herein, we used transfer learning to create precise supervised predictive ANN regression models for water productivity (L/m2.day) predictions based on literature findings. Such observation datasets from single-basin solar stills were utilized to build the random initialization ANN model. The transfer learning method was applied to the latter model by taking the learned network (weights) for fine-tuning the hyperparameters from the earlier developed novel hybrid solar still known as the source (pre-trained) ANN model, to predict the target ANN model. Based on most minor statistical errors, the pre-trained model with 5–64–64-1 architecture and ReLU activation function was the most appropriate for water productivity prediction. All created ANN models were compared to the MLR model. The results revealed that the generated target ANN model outperformed the ANN RI and MLR with OI values of 0.872, 0.834, and 0.803, respectively, in all modeling stages. The target ANN model's accuracy and generalization were sufficient. The target ANN model had residuals of forecasted distillate values of around 1%. This work discusses the significance of transfer learning to generate accurate target ANN models for predicting freshwater outputs in single-slope solar stills, which can be integrated with established theoretically tuned parameters to enhance performance and maximize distillate water yields.
Read or Download: PDF