Empowering Neural Networks with Control and Planning Abilities
In NeurIPS 2024 Workshop on Behavioral ML (non-archival),
Shuyuan Wang, Philip D Loewen, Bhushan Gopaluni, Michael Forbes
[PDF]
Click to enlarge image.
Abstract
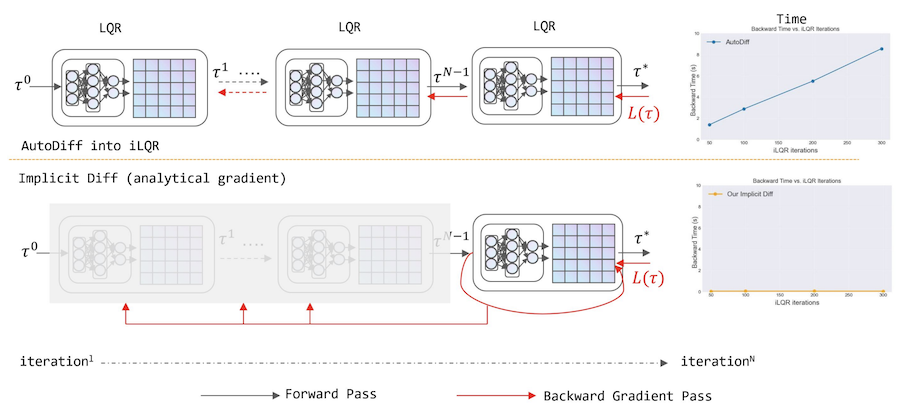
Learning effective behaviors requires both adaptability and structured planning, traditionally split between model-free and model-based methods. Differentiable control combines the strengths of both, but iLQR, a powerful nonlinear controller, lacks differentiability, limiting its use in end-to-end learning. Differentiating through extended iterations introduces scalability challenges, further hindering its application. We propose a framework that enables iLQR to function as a trainable and differentiable module, either as or within a neural network, by using implicit differentiation to compute accurate gradients with constant backward cost. On behavior imitation tasks across standard benchmarks, our method achieves up to 128x speedup (minimum 21x) over automatic differentiation and improves learning efficiency by 106x compared to conventional neural policies. This framework equips neural networks with control and planning abilities, bridging control theory and behavioral learning.
Read or Download: PDF