Time Series Representation Learning Via Cross-Domain Predictive and Contextual Contrasting: Application to Fault Detection
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 149, pp. 110425,
Ibrahim Yousef, Sirish L. Shah, and R. Bhushan Gopaluni
[PDF] [Code]
Click to enlarge image.
Abstract
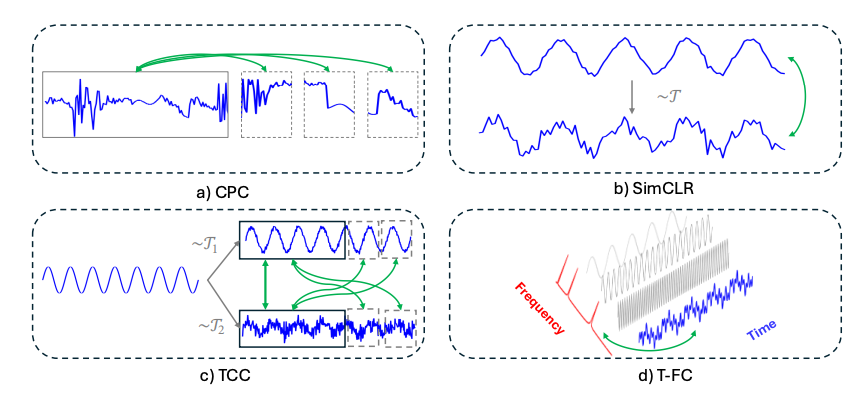
Data-driven methods for fault detection increasingly rely on large historical datasets, yet annotations are costly and time-consuming. As a result, learning approaches that minimize the need for extensive labeling, such as self-supervised learning (SSL), are becoming more popular. Contrastive learning, a subset of SSL, has shown promise in fields like computer vision and natural language processing (NLP), yet its application in fault detection is not fully explored. In this paper, we introduce Cross-Domain Predictive and Contextual Contrasting (CDPCC), a novel contrastive learning framework that integrates temporal and spectral information to capture rich time-frequency features from time series data. CDPCC consists of two key components: cross-domain predictive contrasting, which predicts future embeddings across time and frequency domains, and cross-domain contextual contrasting, which aligns time- and frequency-based representations in a shared latent space. We evaluate CDPCC on fault detection tasks using both simulated and industrial datasets. Our results show that a linear classifier trained on features learned by CDPCC performs comparably to fully supervised models. Moreover, CDPCC proves highly effective in scenarios with limited labeled data, achieving superior performance with only 50% of the labeled data compared to fully supervised training on the entire dataset.
Read or Download: PDF