Anomaly detection for drilling tools based on operating mode recognition and interval-augmented Mahalanobis distance
Control Engineering Practice,
Wenkai Hu, Bin Hu, Yupeng Li, Peng Zhang, R. Bhushan Gopaluni and Weihua Cao
[PDF]
Abstract
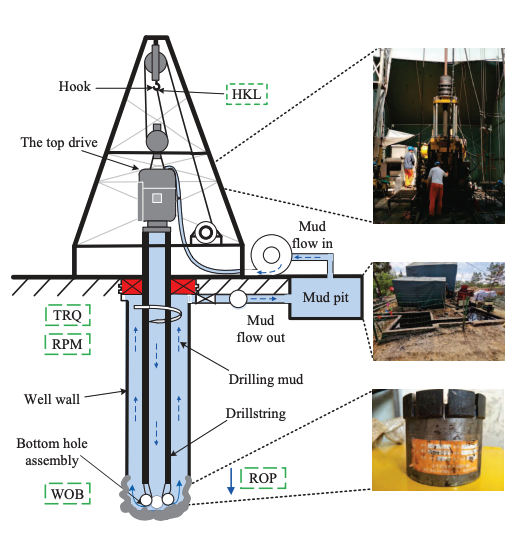
Prompt and accurate anomaly detection of drilling tools is of great significance to ensure the safe and stable operation of drilling processes. However, the operating mode of a drilling tool may often change, leading to difficulties in distinguishing the drilling anomalies from the normal mode switching. Further, the variations of drilling signals caused by such anomalies in drilling tools are usually slight, making it quite challenging to separate the abnormal part from the normal part in the time series, which would compromise the accuracy and promptness of anomaly detection. Accordingly, this paper proposes a new method for anomaly detection of drilling tools based on operating mode recognition and interval-augmented Mahalanobis distance. The main contributions are threefold: 1) A mode recognition method based on the Earth Mover’s distance (EMD) and K-means clustering is proposed to identify drilling operating modes. 2) An anomaly detection method based on the interval-augmented Mahalanobis distance (IAMD) is proposed to detect anomalies of drilling tools. 3) An alarm generation strategy based on the kernel density estimation and alarm deadband is designed to reduce the false alarm rate. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated by industrial case studies involving a real drilling system.
Read or Download: PDF